 PDF(4593 KB)
PDF(4593 KB)


新一代±800 kV/8 GW特高压直流换流阀用饱和电抗器温升试验及比对分析
刘帮虎, 王加龙, 潘励哲, 杨勇, 石岩, 李明
电力建设 ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (10) : 90-97.
 PDF(4593 KB)
PDF(4593 KB)
 PDF(4593 KB)
PDF(4593 KB)
新一代±800 kV/8 GW特高压直流换流阀用饱和电抗器温升试验及比对分析
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Temperature Rise Test and Comparative Analysis of Saturable Reactors for New Generation of ±800 kV/8 GW UHVDC Converter Valve
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}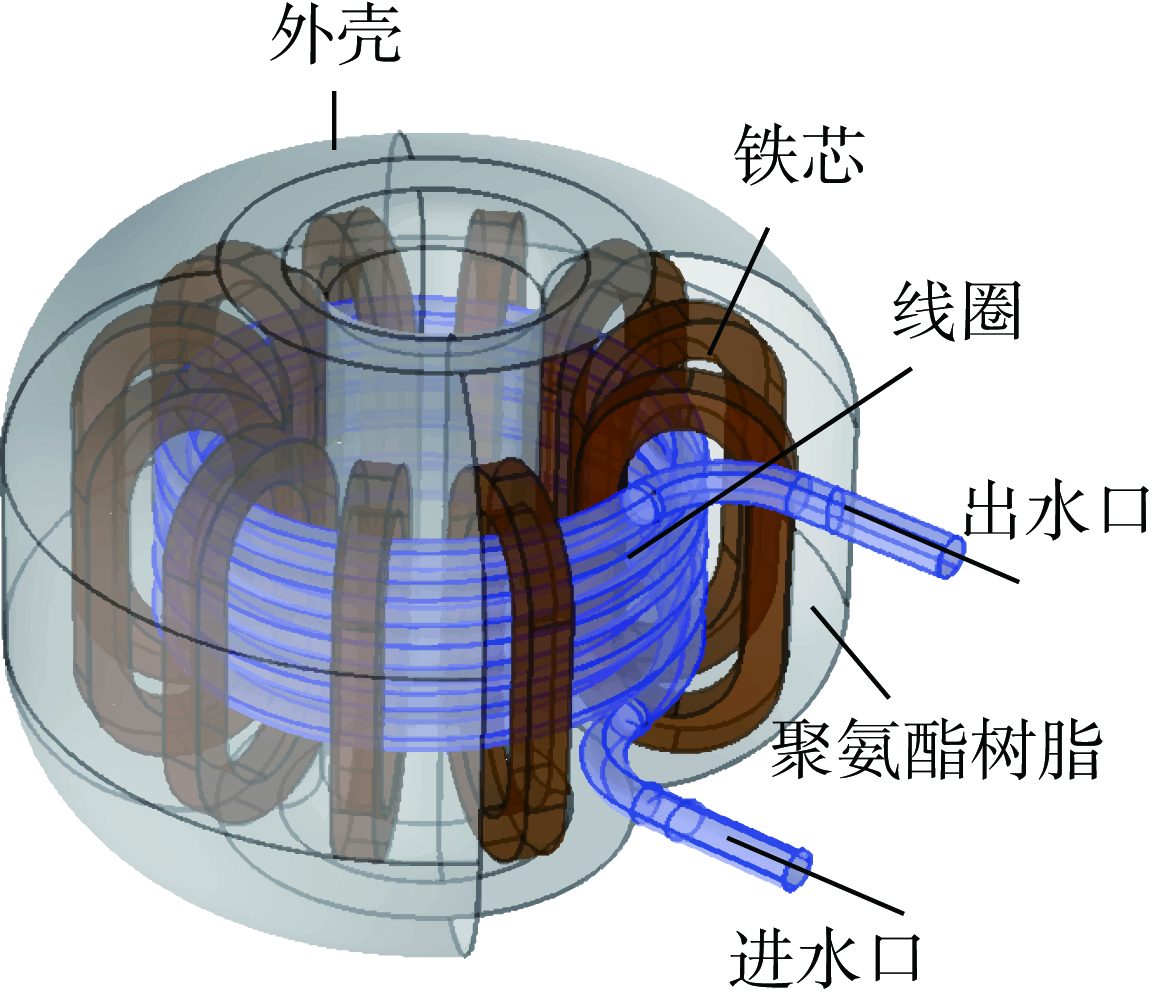
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |