 PDF(4645 KB)
PDF(4645 KB)


欧洲电网的发展及其与全球能源互联网的兼容性
韩正一, CRESPI Giulia, 黄涛, 谭新, 马志远, 杨方, 黄瀚
电力建设 ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (11) : 60-70.
 PDF(4645 KB)
PDF(4645 KB)
 PDF(4645 KB)
PDF(4645 KB)
欧洲电网的发展及其与全球能源互联网的兼容性
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Development of European Power Grid and Its Compatibility with Global Energy Interconnection
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}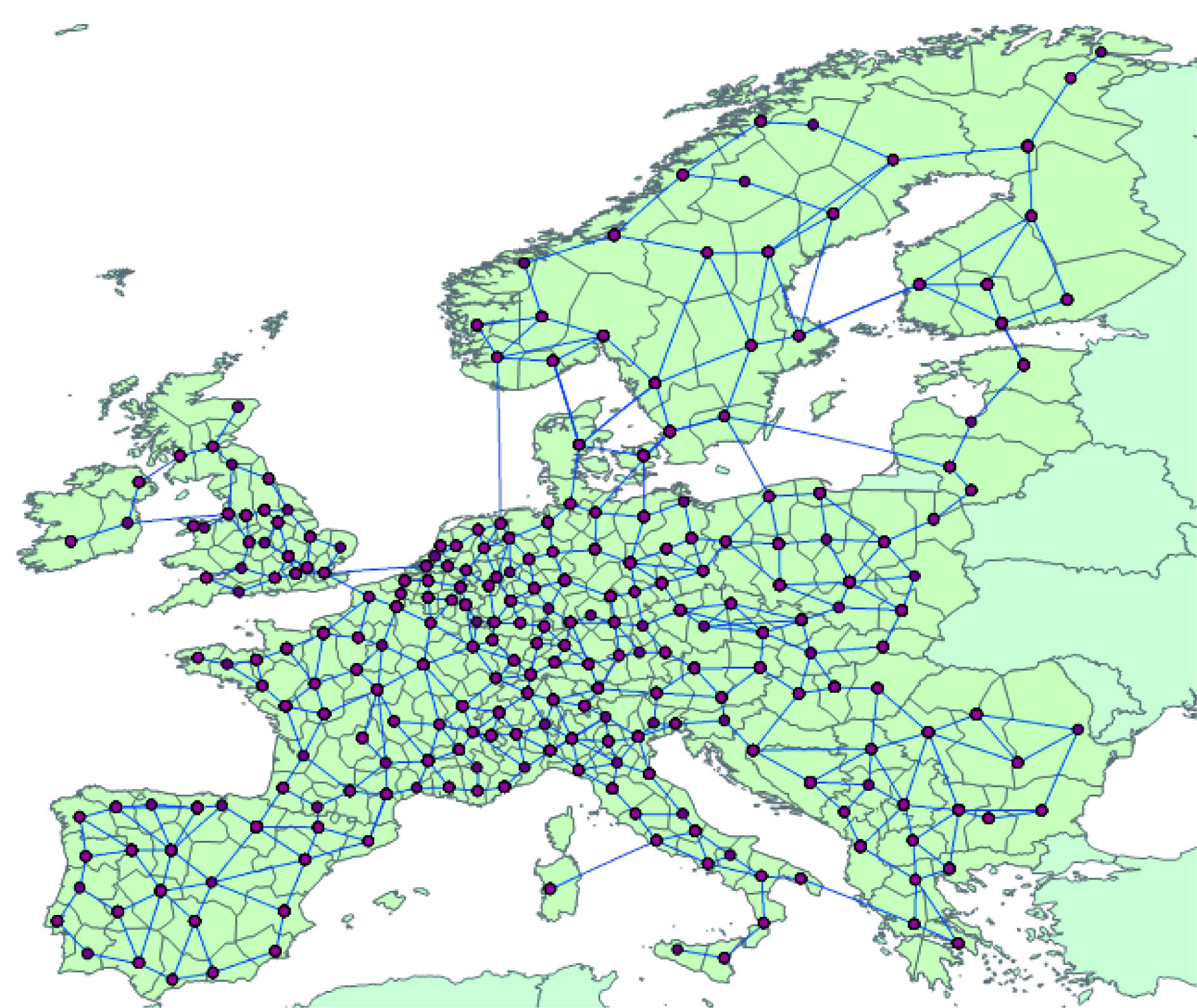
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |