WANG Bingyu, YAN Yong, WEN Fushuan, ZHOU Ziqiang, LIN Shaowa, CHEN Xingying
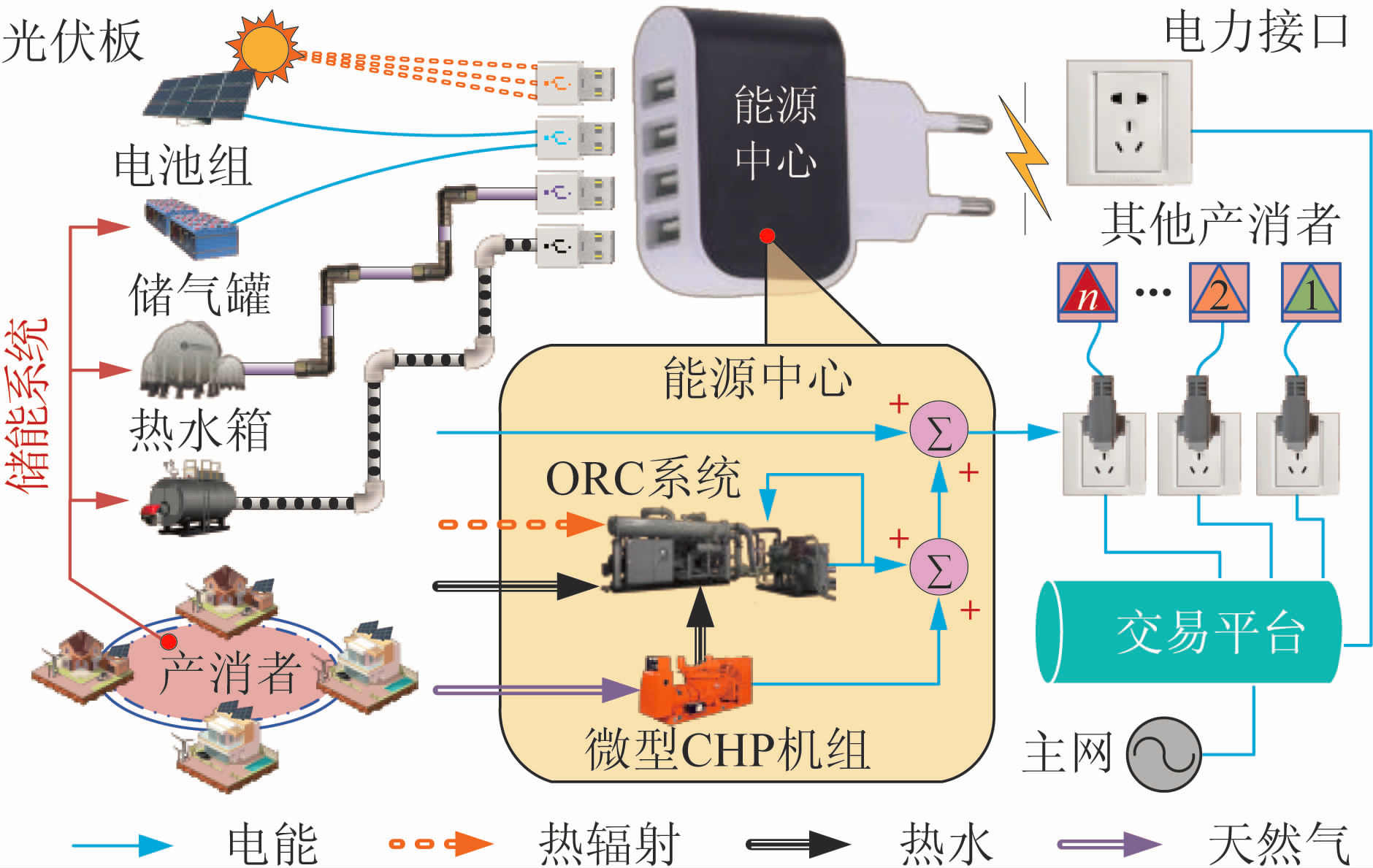
With the rapid development of photovoltaic (PV) power generation and the gradual downward subsidies, the advantages of satisfying load demand by local generation supply are becoming more and more significant, and market trading for distributed generation (MTDG) is then promoted. In MTDG, both power generation and load demand are located at the end of the utility grid, with some features exhibited including numerous participating entities, small transaction sizes, and point-to-point transactions. The traditional centralized transaction model suffers some problems such as low transparency, high cost, low efficiency, and untrustworthy data, and is not suitable for MTDG. Blockchain technology has the characteristics of decentralization, non-tampering, and anonymity, and can well meet the needs of MTDG for improved security, autonomy and transparency of electricity transactions. Given this background, the blockchain technology is applied in MTDG, and the corresponding trading mechanism, settlement mechanism and reward and punishment mechanism are developed considering the characteristics of MTDG. Finally, an example is employed to demonstrate the developed MTDG mechanism.