
Monthly
ISSN 1000-7229
CN 11-2583/TM
- CSCD核心库收录期刊
- 中文核心期刊
- 中国科技核心期刊


Monthly
ISSN 1000-7229
CN 11-2583/TM

ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 39-57.doi: 10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2024.03.004
• Energy Quality Theory and Its Low-Carbon and High-Efficiency Application in Integrated EnergySystems?Hosted by Associate Professor WANG Dan, Professor CHEN Qicheng, Associate Professor HU Xiao and Associate Professor YU Jie? • Previous Articles Next Articles
GAO Jianwei1,2, HUANG Ningbo1,2( ), GAO Fangjie1,2, WU Haoyu1,2, MENG Qichen1,2, LIU Jiangtao1,2
), GAO Fangjie1,2, WU Haoyu1,2, MENG Qichen1,2, LIU Jiangtao1,2
Received:2023-08-08
Published:2024-03-01
Online:2024-02-28
Supported by:CLC Number:
GAO Jianwei, HUANG Ningbo, GAO Fangjie, WU Haoyu, MENG Qichen, LIU Jiangtao. Selection of Economics-Energy-Environment Scheduling Strategy for a Community Virtual Power Plant Considering Decision-makers’ Risk Attitudes Based on Improved Information Gap Decision Theory[J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2024, 45(3): 39-57.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.cepc.com.cn/EN/10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2024.03.004
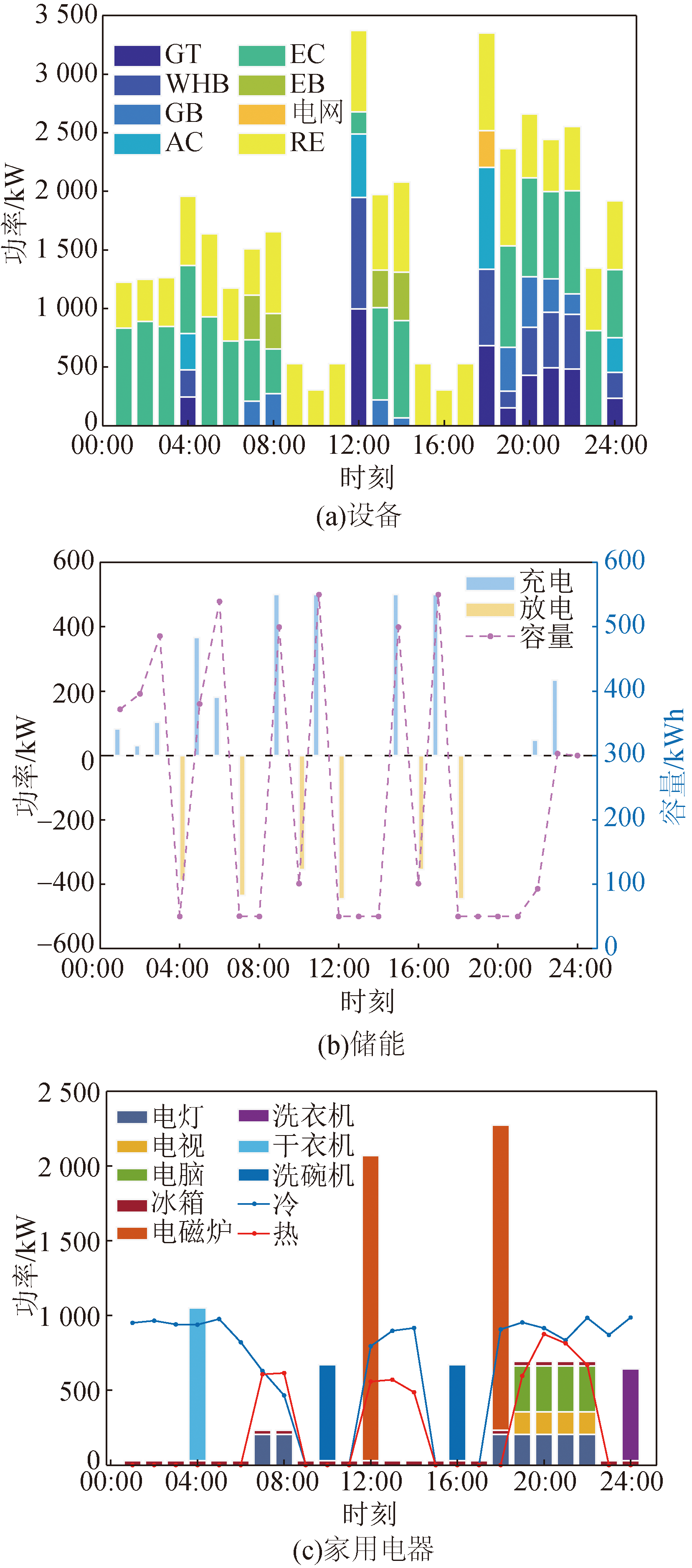
Fig.6 Equipment output and household appliances operation after multiple objectives optimization with considering uncertain factors-conservative decision-makers

Fig.7 Equipment output and household appliances operation after multiple objectives optimization with considering uncertain factors-risk decision-makers
| [1] |
GAO J W, GAO F J, MA Z Y, et al. Multi-objective optimization of smart community integrated energy considering the utility of decision makers based on the Lévy flight improved chicken swarm algorithm[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021, 72: 103075.
doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2021.103075 URL |
| [2] | 国家发展和改革委员会, 国家能源局. 关于促进智能电网发展的指导意见(发展改革行动[2015]1518)[EB/OL]. (2015-07-07)[2023-07-20]. http://www.nea.gov.cn/2015-07/07/c_134388049.htm. |
| [3] |
KIM I, JAMES J A, CRITTENDEN J. The case study of combined cooling heat and power and photovoltaic systems for building customers using HOMER software[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2017, 143: 490-502.
doi: 10.1016/j.epsr.2016.10.061 URL |
| [4] |
MATAMALA Y, FEIJOO F. A two-stage stochastic Stackelberg model for microgrid operation with chance constraints for renewable energy generation uncertainty[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 303: 117608.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117608 URL |
| [5] |
WANG Z K, CRAWLEY J, LI F G N, et al. Sizing of district heating systems based on smart meter data: quantifying the aggregated domestic energy demand and demand diversity in the UK[J]. Energy, 2020, 193: 116780.
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.116780 URL |
| [6] | 刘蓉晖, 李阳, 杨秀, 等. 考虑需求响应的社区综合能源系统两阶段优化调度[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42(9): 46-54. |
| LIU Ronghui, LI Yang, YANG Xiu, et al. Two-stage optimal dispatching of community comprehensive energy system considering demand response[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42(9): 46-54. | |
| [7] |
GAO F J, GAO J W, ZHANG Y, et al. Community decision-makers’ choice of multiple objectives scheduling strategy for integrated energy considering multiple uncertainties and demand response[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2022, 83(8):103945.
doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2022.103945 URL |
| [8] |
JU L W, ZHAO R, TAN Q L, et al. A multi-objective robust scheduling model and solution algorithm for a novel virtual power plant connected with power-to-gas and gas storage tank considering uncertainty and demand response[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 250: 1336-1355.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.05.027 URL |
| [9] | 唐虎, 陈爱伦, 崔浩, 等. 社区型能源互联网下的虚拟电厂参与电力市场策略分析[J]. 南方能源建设, 2019, 6(3): 40-47. |
| TANG Hu, CHEN Ailun, CUI Hao, et al. Strategy analysis of virtual power plants participation in electric power market with community energy internet[J]. Southern Energy Construction, 2019, 6(3): 40-47. | |
| [10] |
MONIE S, NILSSON A M, WIDÉN J, et al. A residential community-level virtual power plant to balance variable renewable power generation in Sweden[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 228: 113597.
doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113597 URL |
| [11] |
GONG H J, JONES E S, ALDEN R E, et al. Virtual power plant control for large residential communities using HVAC systems for energy storage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2022, 58(1): 622-633.
doi: 10.1109/TIA.2021.3120971 URL |
| [12] |
LIU C M, WANG C L, YIN Y J, et al. Bi-level dispatch and control strategy based on model predictive control for community integrated energy system considering dynamic response performance[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 310: 118641.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.118641 URL |
| [13] | 缴傲, 胡臻, 向萌, 等. 考虑综合需求响应的社区综合能源系统主从博弈策略[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2021, 33(9): 94-102. |
| JIAO Ao, HU Zhen, XIANG Meng, et al. Master-slave game strategy for community integrated energy system considering integrated demand response[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2021, 33(9): 94-102. | |
| [14] | 陈华, 黄海晔. 考虑碳排放的社区级综合能源系统优化模型[J]. 上海电力大学学报, 2020, 36(6): 613-618. |
| CHEN Hua, HUANG Haiye. Optimal operation of community-level comprehensive energy systems considering carbon emissions[J]. Journal of Shanghai University of Electric Power, 2020, 36(6): 613-618. | |
| [15] |
FAYYAZ ROUHBAKHSH F, HASSANPOUR H, EFFATI S. Some new solution concepts in generalized fuzzy multiobjective optimization problems[J]. Soft Computing, 2018, 22(10): 3261-3270.
doi: 10.1007/s00500-017-2787-0 URL |
| [16] |
ZHOU Y Z, WEI Z N, SUN G Q, et al. A robust optimization approach for integrated community energy system in energy and ancillary service markets[J]. Energy, 2018, 148: 1-15.
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.01.078 URL |
| [17] |
AIEN M, HAJEBRAHIMI A, FOTUHI-FIRUZABAD M. A comprehensive review on uncertainty modeling techniques in power system studies[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 57: 1077-1089.
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.070 URL |
| [18] |
TAJEDDINI M A, RAHIMI-KIAN A, SOROUDI A. Risk averse optimal operation of a virtual power plant using two stage stochastic programming[J]. Energy, 2014, 73: 958-967.
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2014.06.110 URL |
| [19] |
TAN Z F, FAN W, LI H F, et al. Dispatching optimization model of gas-electricity virtual power plant considering uncertainty based on robust stochastic optimization theory[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 247: 119106.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119106 URL |
| [20] |
AGUILAR J, BORDONS C, ARCE A. Chance constraints and machine learning integration for uncertainty management in virtual power plants operating in simultaneous energy markets[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2021, 133: 107304.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2021.107304 URL |
| [21] |
ZHANG Y, YUAN F M, ZHAI H P, et al. Optimizing the planning of distributed generation resources and storages in the virtual power plant, considering load uncertainty[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 387: 135868.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.135868 URL |
| [22] |
VAHEDIPOUR-DAHRAIE M, RASHIDIZADEH-KERMANI H, ANVARI-MOGHADDAM A, et al. Risk-averse probabilistic framework for scheduling of virtual power plants considering demand response and uncertainties[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2020, 121: 106126.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2020.106126 URL |
| [23] | 于雪菲, 张帅, 刘琳琳, 等. 基于信息间隙决策理论的碳捕集电厂调度[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 62(9): 1467-1473. |
| YU Xuefei, ZHANG Shuai, LIU Linlin, et al. Carbon capture power plant scheduling based on information gap decision theory[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2022, 62(9): 1467-1473. | |
| [24] | BEN-HAIM Y. Info-gap decision theory: decisions under severe uncertainty[M]. Academic Press, 2006. |
| [25] | 秦绍基, 林靖淳, 张勇军, 等. 基于熵权自适应信息间隙决策的园区综合能源系统规划[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47(10): 4190-4203. |
| QIN Shaoji, LIN Jingchun, ZHANG Yongjun, et al. Comprehensive energy system planning of park based on entropy weight adaptive information gap decision[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47(10): 4190-4203. | |
| [26] |
FATHI R, TOUSI B, GALVANI S. A new approach for optimal allocation of photovoltaic and wind clean energy resources in distribution networks with reconfiguration considering uncertainty based on info-gap decision theory with risk aversion strategy[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 295: 125984.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.125984 URL |
| [27] |
KAHNEMAN D, TVERSKY A. Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk[J]. Econometrica, 1979, 47(2): 263.
doi: 10.2307/1914185 URL |
| [28] |
LIN B Q, JIA Z J. Is emission trading scheme an opportunity for renewable energy in China? A perspective of ETS revenue redistributions[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 263: 114605.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114605 URL |
| [29] |
GOU X J, XU Z S, WANG X X, et al. Managing consensus reaching process with self-confident double hierarchy linguistic preference relations in group decision making[J]. Fuzzy Optimization and Decision Making, 2021, 20(1): 51-79.
doi: 10.1007/s10700-020-09331-y |
| [30] | 王铁旦, 李诗瑶, 彭定洪. 基于BB-VIKOR法的新型智慧城市建设质量评价研究[J]. 昆明理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2022, 22(3): 96-105. |
| WANG Tiedan, LI Shiyao, PENG Dinghong. Research on the quality evaluation of new smart city construction based on BB-VIKOR method[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Social Sciences), 2022, 22(3): 96-105. | |
| [31] | 缑迅杰, 邓富民, 徐泽水. 基于自信双层语言偏好关系的大规模群体共识决策方法及其应用研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2023, 31(9): 222-232. |
| GOU Xunjie, DENG Fumin, XU Zeshui. The application of the large-scale group consensus decision-making method based on self-confident double hierarchy linguistic preference relations[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2023, 31(9): 222-232. | |
| [32] |
OPRICOVIC S, TZENG G H. Extended VIKOR method in comparison with outranking methods[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2007, 178(2): 514-529.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2006.01.020 URL |
| [33] |
GOU X J, LIAO H C, XU Z S, et al. Group decision making with double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations: consistency based measures, index and repairing algorithms and decision model[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 489: 93-112.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.03.037 URL |
| [34] |
MILLET I. The effectiveness of alternative preference elicitation methods in the analytic hierarchy process[J]. Journal of Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis, 1997, 6(1): 41-51.
doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1360(199701)6:1<41::AID-MCDA122>3.0.CO;2-D URL |
| [35] |
CHICLANA F, HERRERA-VIEDMA E, ALONSO S, et al. Cardinal consistency of reciprocal preference relations: a characterization of multiplicative transitivity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2009, 17(1): 14-23.
doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2008.2008028 URL |
| [36] |
尹儇鹏, 徐选华, 陈晓红. 风险视域下的大群体应急决策策略选择研究[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2021, 41(3): 678-690.
doi: 10.12011/SETP2019-0940 |
| YIN Xuanpeng, XU Xuanhua, CHEN Xiaohong. Study on the selection of large group emergency decision-making strategies under the perspective of risk[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2021, 41(3): 678-690. | |
| [37] | 梅文明, 李美成, 张宇威, 等. 基于前景理论和VIKOR法的多能源微电网效益评价[J]. 供用电, 2020, 37(3): 71-77. |
| MEI Wenming, LI Meicheng, ZHANG Yuwei, et al. Benefit evaluation of multi energy microgrid based on prospect theory and VIKOR method[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2020, 37(3): 71-77. |
| [1] | ZHANG Zhiyi, DOU Zhenhai, YU Runze, HU Yachun, CHEN Jiajia, YIN Wenliang. Low-carbon Economic Dispatch of Integrated Energy System Considering Electric-thermal Equivalent Virtual Energy Storage [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2024, 45(3): 16-26. |
| [2] | WANG Limeng, LIU Xuemeng, LI Yang, CHANG Duo, REN Xing. Low-Carbon Optimal Dispatch of Integrated Energy System Considering Demand Response under the Tiered Carbon Trading Mechanism [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2024, 45(2): 102-114. |
| [3] | KANG Yiming, QIN Wenping, YAO Hongmin, XING Yahong, HU Yingying, JIA Xingping. Source-Grid-Load Multi-agent Coordinated Interactive Planning in Power Market Environment [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2024, 45(2): 147-159. |
| [4] | REN Hongbo, WANG Nan, WU Qiong, SHI Shanshan, FANG Chen, WAN Sha. Collaborative Optimal Scheduling and Cost Allocation of Multiload Aggregator Considering Ladder-Type Carbon Trading [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2024, 45(2): 171-182. |
| [5] | DU Weizhu, BAI Kai, LI Haibo, ZHANG Lei, LIU Di, SHI Xintao. Source-Load-Storage Flexible Resource Optimization Planning that Takes into Account Power Supply and Accommodation [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2023, 44(9): 13-23. |
| [6] | SHU Junlin, LIU Junyong, GAO Hongjun, HE Xin, HU Renchuan. Distributionally Robust Optimal Operation of Distribution Network Considering Switch Reconfiguration and Demand Response [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2023, 44(6): 101-111. |
| [7] | LIU Ren, LIU Yang, XU Lixiong, LI Zhenwei, LI Xueling. Multi-microgrid System Collaborative Optimization Strategy Considering Distributed Demand Response [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2023, 44(5): 72-83. |
| [8] | CUI Wenqian, WEI Junqiang, ZHAO Yunhao, GAO Wei, CHEN Kang. Multi-objective Operation Optimization of Distribution Network with Gravity Energy Storage under Double Carbon Target [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2023, 44(4): 45-53. |
| [9] | FAN Xinyu, HUANG Yuan, WU Jiang, SUN Zengjie, NING Jingbo. Resilience Promotion Strategy for Distribution Network Considering Source-Network-Load-Storage Coordination [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2023, 44(4): 63-73. |
| [10] | YUAN Xiyao, WANG Guantao, ZHU Ruoyuan, BAI Xingzhen, GE Leijiao, LI Guhui. Optimal Scheduling of Park Integrated Energy System with P2G Waste Heat Recovery and Demand Response under Carbon-Green Certificate Trading Mechanism [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2023, 44(3): 25-35. |
| [11] | YAO Yin, ZHU Yedong, LI Dongdong, ZHOU Bo, LIN Shunfu. Multi-scenario Demand Response Strategy Based on DEMATEL-AISM for Electric Vehicles [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2023, 44(3): 93-104. |
| [12] | FAN Wei, LI Xudong, WANG Yao, LI Xiangguang, WANG Yujie, TAN Zhongfu, JU Liwei. Two-Stage Scheduling Optimization Model of Flexible Resource Aggregation in New Power System [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2023, 44(2): 25-37. |
| [13] | JIN Bingjie, LI Jiaxing, PENG Hongqiao, LUO Shuxin, LU Zhilin, LENG Yuan, DONG Ping, LIANG Ziyang. Cost-Benefit Analysis of Multiple Entities Under the Coupling of Electricity and Carbon Trading Market Considering Demand Response [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2023, 44(2): 50-60. |
| [14] | YU Haozheng, ZHAO Hanjie, LI Ke, ZHU Xingxu, HUANGFU Xiaowen, FAN Jiangchuan, LI Cuiping, LI Junhui. Carrying Capacity Evaluation of Distribution Network for Distributed Photovoltaic Cluster Considering User-Side Demand Response [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2023, 44(2): 122-130. |
| [15] | YU Bin, WENG Liguo, LIAN Deqiang, WANG Sibin, HUANG Yuan, YAO Haotian. Coordinated Operation Strategy of Multiple Parks Considering Distributed Energy Resources and Price-based Incentive Mechanism [J]. ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION, 2023, 44(2): 145-154. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright @ ELECTRIC POWER CONSTRUCTION Editorial Office
Address: Tower A225, SGCC, Future Science & Technology Park,Beijing, China Postcode:102209 Telephone:010-66602697
Technical support: Beijing Magtech Co.ltd support@magtech.com.cn