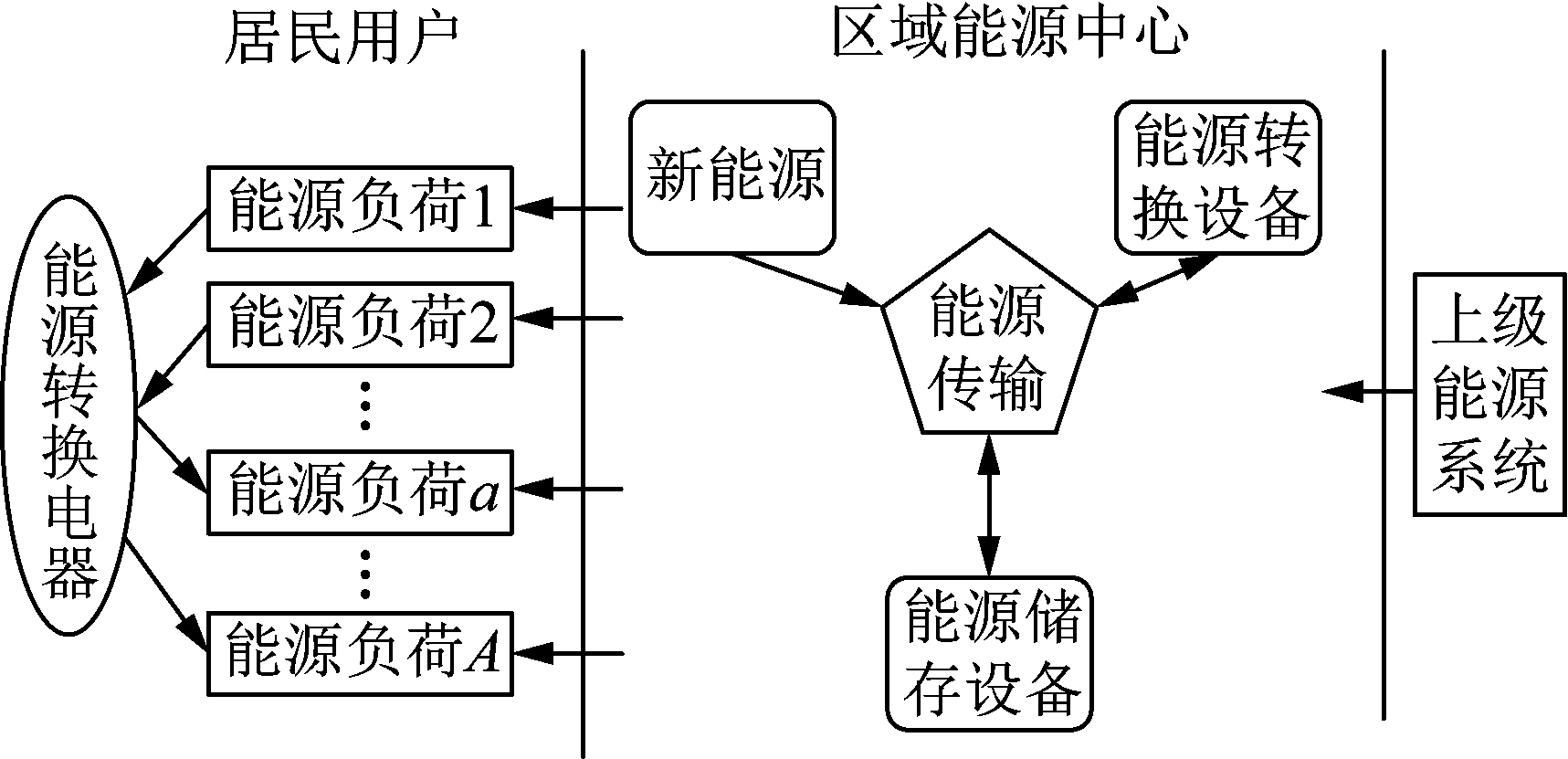
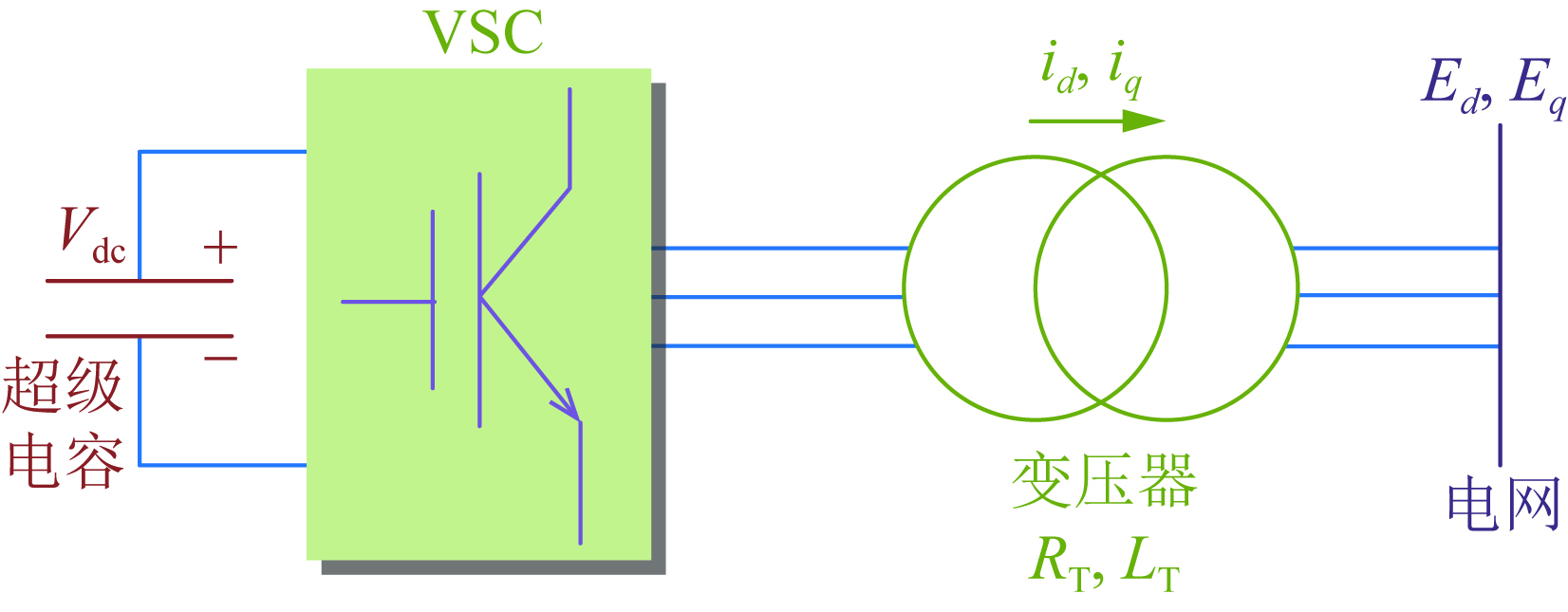
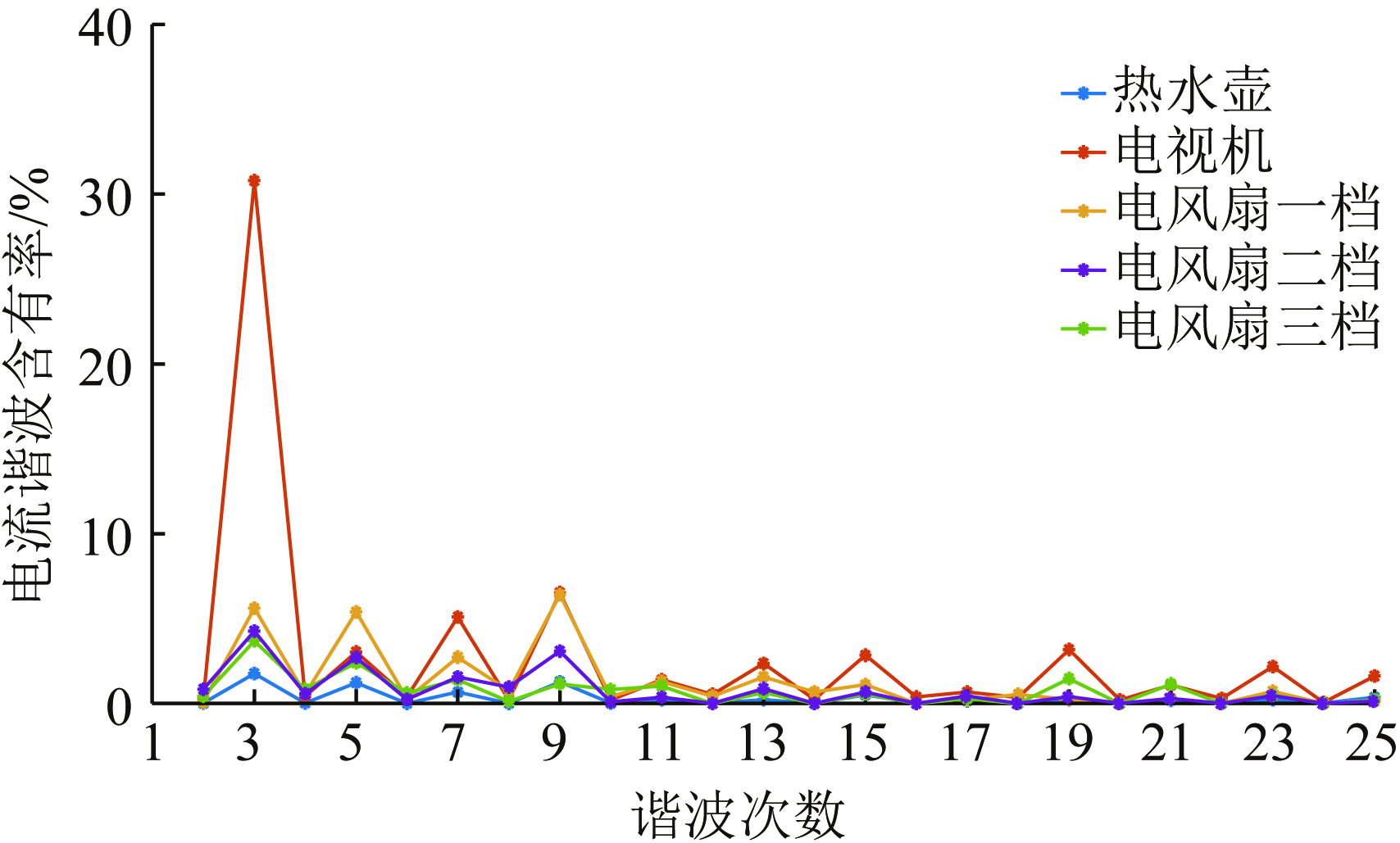
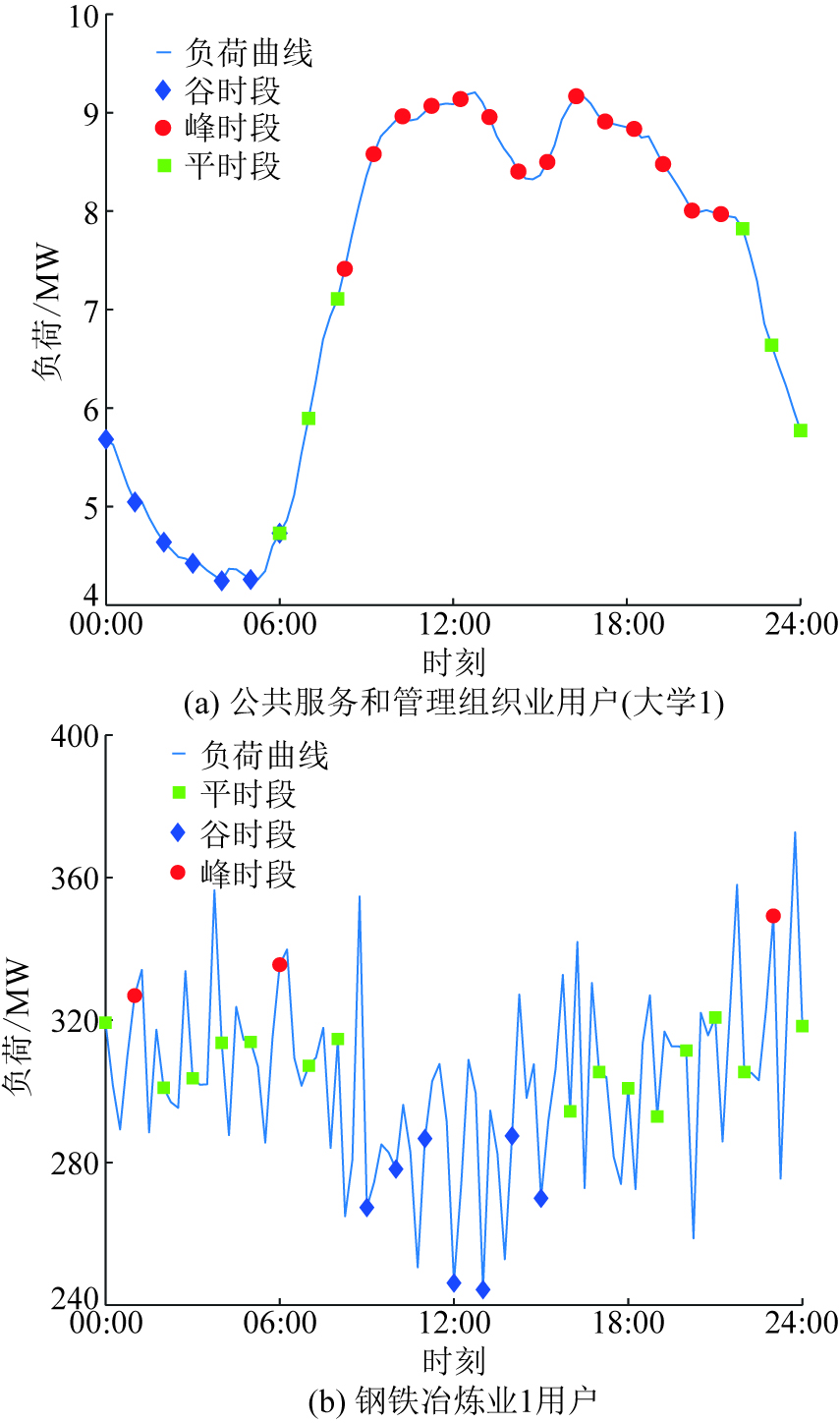
LIU Dunnan, ZHANG Yue, PENG Xiaofeng, LIU Mingguang, WANG Wen, JIA Heping, QIN Guangyu, WANG Jun, YANG Ye
Accurate prediction of electric vehicle charging load has practical significance for power grid dispatching, power market trading, charging station planning and construction. Because the characteristics of electric vehicle charging load are different from the traditional electric load, it is necessary to carry out targeted research on the influencing factors and prediction model of electric vehicle charging load. Considering the differences of time series characteristics and influencing factors of different types of electric vehicle charging load, a prediction model of electric vehicle charging load considering daily type, maximum and minimum temperature is established. Fuzzy C-means (FCM) is used to cluster the charging load, data feature attributes are mined, and similar daily load is extracted. The least square support vector machine (LS-SVM) is used to predict the similar daily load after clustering. The prediction results are compared with the test set, and the results show that the prediction accuracy of the proposed model is higher than that of the LS-SVM method, which verifies the effectiveness of the prediction model.