GUO Mingqun, LAI Qingping, LU Jie, WANG Zhidong, PENG Dong, ZHAO Lang, YU Haiyong
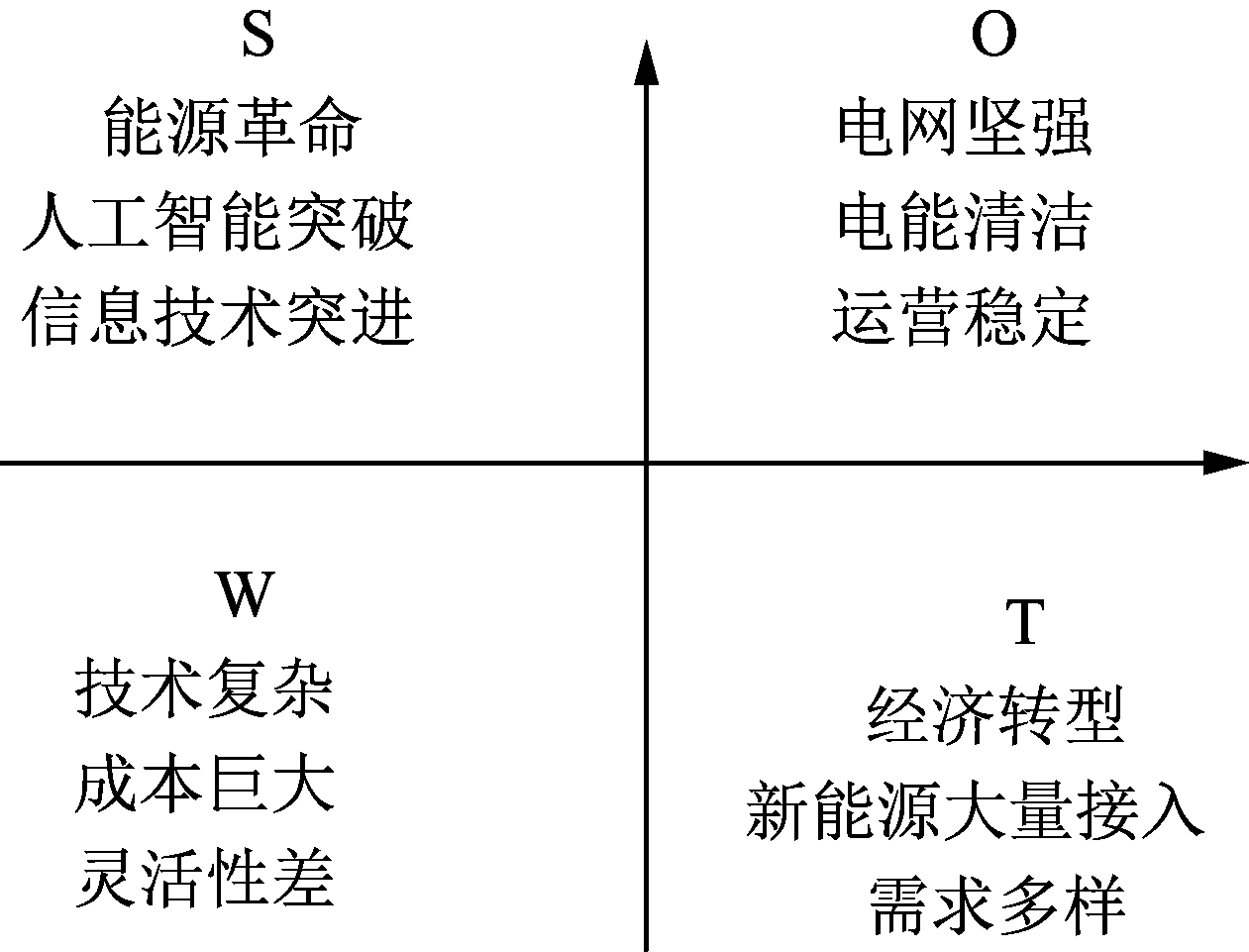
State Grid Corporation of China takes "a leading international energy internet company with Chinese characteristics" as its strategic goal, and proposes important measures such as "continuously improving the level of green electrification" and "promoting energy interconnection" to enable cities with different economic development paths and energy endowment constraints. The distribution network presents a new round of leaping and differentiated development, and it is urgent to study and predict this development form. To this end, this paper uses SWOT technology to analyze the relevant indicators that characterize the operation status of the urban distribution network and the characteristics of the future pattern. An evaluation index system is established from 7 aspects such as power supply quality, grid structure, and equipment level, and then the advantages of the cloud matter element theory is used in the distribution grid assessment. The target is divided into five forms: demonstration, high-level, intermediate, low-level, and primary according to the form classification standard. Finally, three representative cities, Beijing, Suzhou and Hengshui are selected according to the actual development level of the distribution networks from high to low. The results show that the distribution networks of Suzhou and Beijing are both in a demonstration form, but the latter’s green power accommodation is weaker than the former, and all indicators of the Hengshui distribution network are lagging behind and in an intermediate form.




 Author Login
Author Login Peer Review
Peer Review





