LIN Hongyu, YAN Qingyou, DE Gejirifu, YANG Shenbo, WU Jing, FAN Wei, TAN Zhongfu, CUI Zhantao
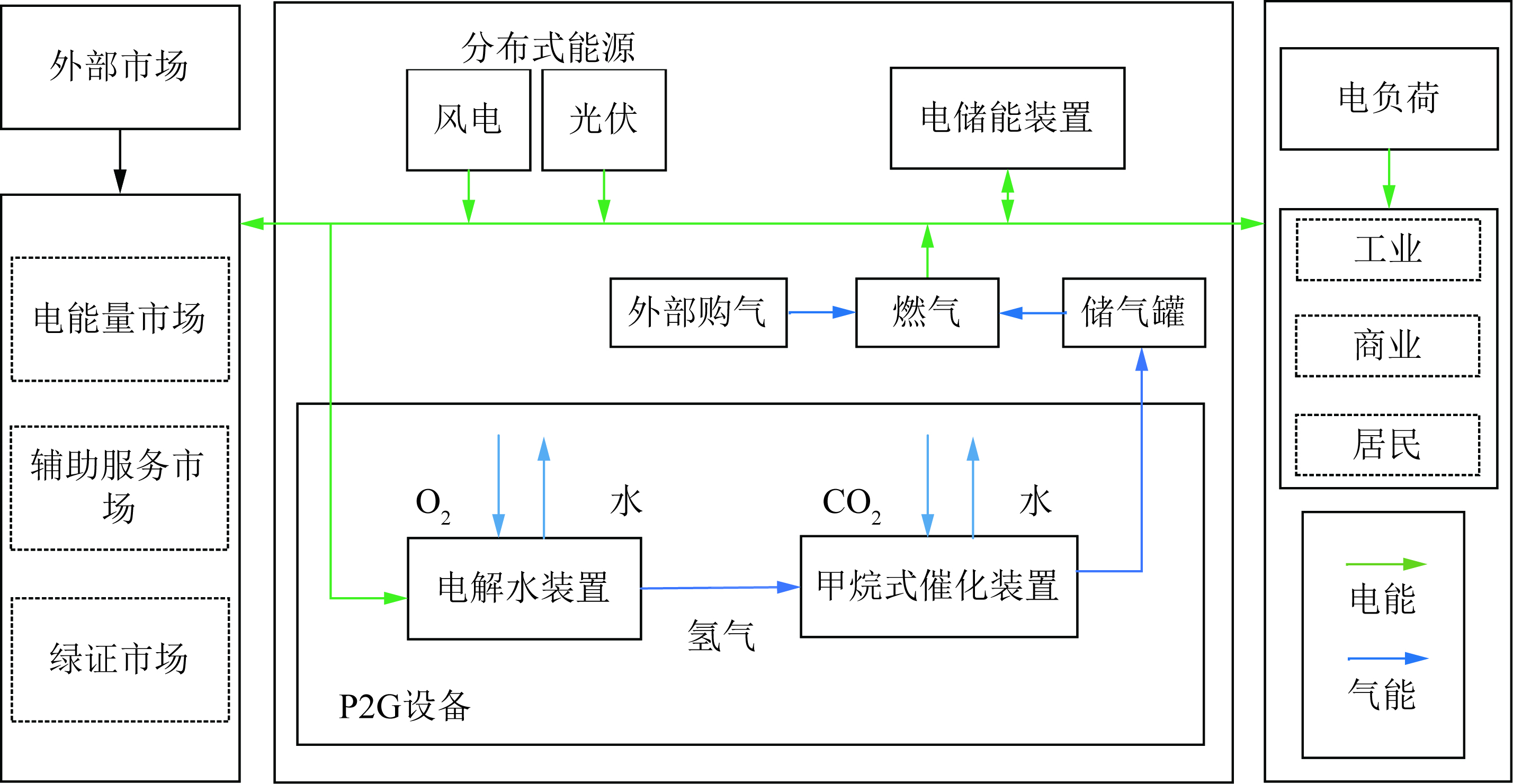
Clean energy power accommodation is a key goal that China has been chasing currently since the power market reform was carried out. Under this background, this paper constructs a peak-regulation optimization model for gas-fired generators in parks with power-to-gas units employed under the mixed market environment. Firstly, the structure of a park power system with photovoltaic and wind power generators, gas-fired generators, a power-to-gas converter, and a gas storage tank is designed. Secondly, with consideration of the green certificate market and peak-regulation compensation mechanism, green certificate trading models for power units in the park and a peak-regulation compensation model are both built. Thirdly, a mathematical model of economic dispatch for park power supply systems with power-to-gas units and clean energy power generation is built, in the pursuit of the minimum CO2 emission and the maximum clean energy power accommodation, peak-regulation willingness of gas-fired generators and system’s revenue. The model is solved by using the chaos particle swarm optimization algorithm. The following results are obtained: 1) the consumption rate of clean energy power has increased 6.69% and the CO2 emission has reduced 14.66 tons, in the scenario with both power-to-gas and peak-regulation compensation mechanism involved; 2) the revenue of the system has increased up to 187,060 Yuan, after fully considering gas-fired generators’ participation in peak regulation, thus verifying the effectiveness of the proposed model and showing a better convergence effect of the algorithm.